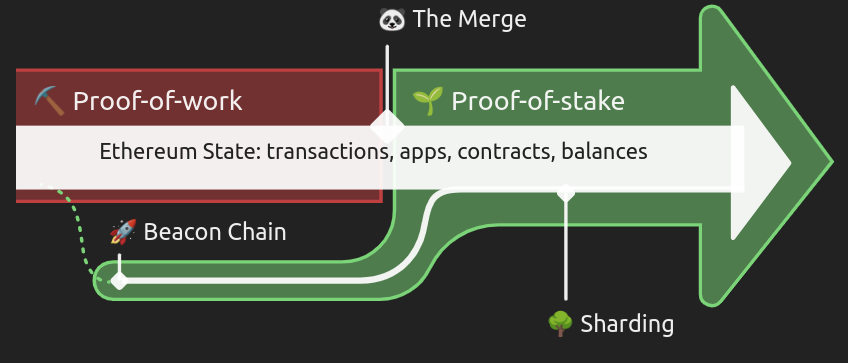
On December 1, 2020, Ethereum shipped the Beacon chain this would then merge with the Mainnet on September 15, 2022, which existed since it was launched in 2015. This and some other events were referred to as “The Merge".

The Beacon Chain.
The Beacon chain was launched on December 2020 to prove whether the idea of Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus logic was sustainable before deploying to Ethereum’s Mainnet. It ran alongside the existing Proof of Work (PoW) consensus but did nothing until The merge was successful.
The Beacon chain was the ledger that coordinated and organized Ethereum-stakers.
The Merge.
“The Merge", as the name suggests was the merging of the Beacon chain and the Mainnet. This meant that Ethereum would henceforth use Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus to validate transaction requests rather than the old Proof of Work that Bitcoin still uses. The Beacon chain ceased to exist after the merge.
It involved:
- All previous miners switched off their workers since Eth is no longer mineable.
- All transactions were prohibited to avoid loss of coins.
- All previous transaction histories from the PoW algorithm since the Genesis block would merge with the new records so that all transactions would be valid.
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake.
In the world of Blockchains, all nodes agree on one state. For this reason, an algorithm is needed, a consensus algorithm is a path that all nodes follow to settle on a joint agreement.
Some of these algorithms are:
- Proof of Work (PoW).
- Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Proof of Authority (PoA).
Proof of Work consensus algorithm.
To validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain, validators have to prove that they have the ability to do so. This could be thought of as trying to unlock a chest. So, the more people making the guesses, the more guesses, the more the chances of getting it right, right?
Back to bitcoin, for you to successfully add new blocks:
one needs very high computing power - this causes a lot of energy waste used to run and cool idle machines this being the largest drawback.
It is important to note that only 21,000,000 bitcoins can exist which was intentional so that to make bitcoin as scarce as Gold and curb inflation, this can only change if the protocal is changed.
The tragedy of commons.
In the future probably by 2050, bitcoin will hit the 21,000,000 mark. This is a good and a bad thing, it will mean that there will be no bounties for creating new blocks and miners will only earn transaction fees. This could result in miners leaving the pool for other more profitable pools with time fewer miners will mine bitcoin thus decreasing the network difficulty which would leave bitcoin exposed to the 51% attack.
Proof of Stake consensus algorithm.
Ethereum switched to Proof of Stake there were some primary reasons behind that but we’ll get to that in a minute.
Unlike Proof of Work, this way of reaching a consensus does not need a lot of computing power since a validator is chosen quickly.
To become a validator, you have to invest in buying a network stake of 32 ETH as the case in Ethereum, the more the coins .. the more the chances of being selected as the next validator. However, this is not the only criteria used to determine the next validator since it would favor those with more stake -The rich.
Nodes are randomly selected to be validators of the next block based on:
- The staking age.
- Randomization.
- The node’s wealth.
These three factors ensure that choosing the next validator is fair & square. Still, those with more coins are favored but better than the Proof of Work consensus which favors those with high computation power & more electricity.
Ethereum and Proof of Stake.
The main reasons for the merge were:
- Making Ethereum green means less energy consumption, especially energy from non-renewable sources.
- To make Ethereum more scalable is by improving the transaction speeds, reaching a consensus does not need workers.
It’s important to note that Proof of Stake does not make Ethereum faster as it does not affect the network capacity.
