What is topology
A network topology is a substantial network arrangement in which all the nodes are connected using network links or connecting lines. Apart from just describing how the nodes are interconnected, network topology also explains how the data is transferred in a network.
Logical topology
Also called signal topology deals with the way data passes from one device to the next on the network. examples are Ethernet and token rings.
Ethernet topology
In internet topology, all computers listen to the network media and can only send data when none others are sending.
Token ring topology
In a token ring topology, a special package for data called a token goes around the network, and only the computers whose address is on the data held in the token will take up the token to read the data and then release the token. the token can then be captured by another computer that needs to transmit data.
Physical topology
Refers to the Physical layout or arrangement of components on the network. examples include star, bus, ring, mesh, and tree topologies.
Star topology
In star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub. Nodes communicate across the network by passing data through the hub. when the hub receives data from a transmitting computer, it broadcasts the message to all the other nodes on the network
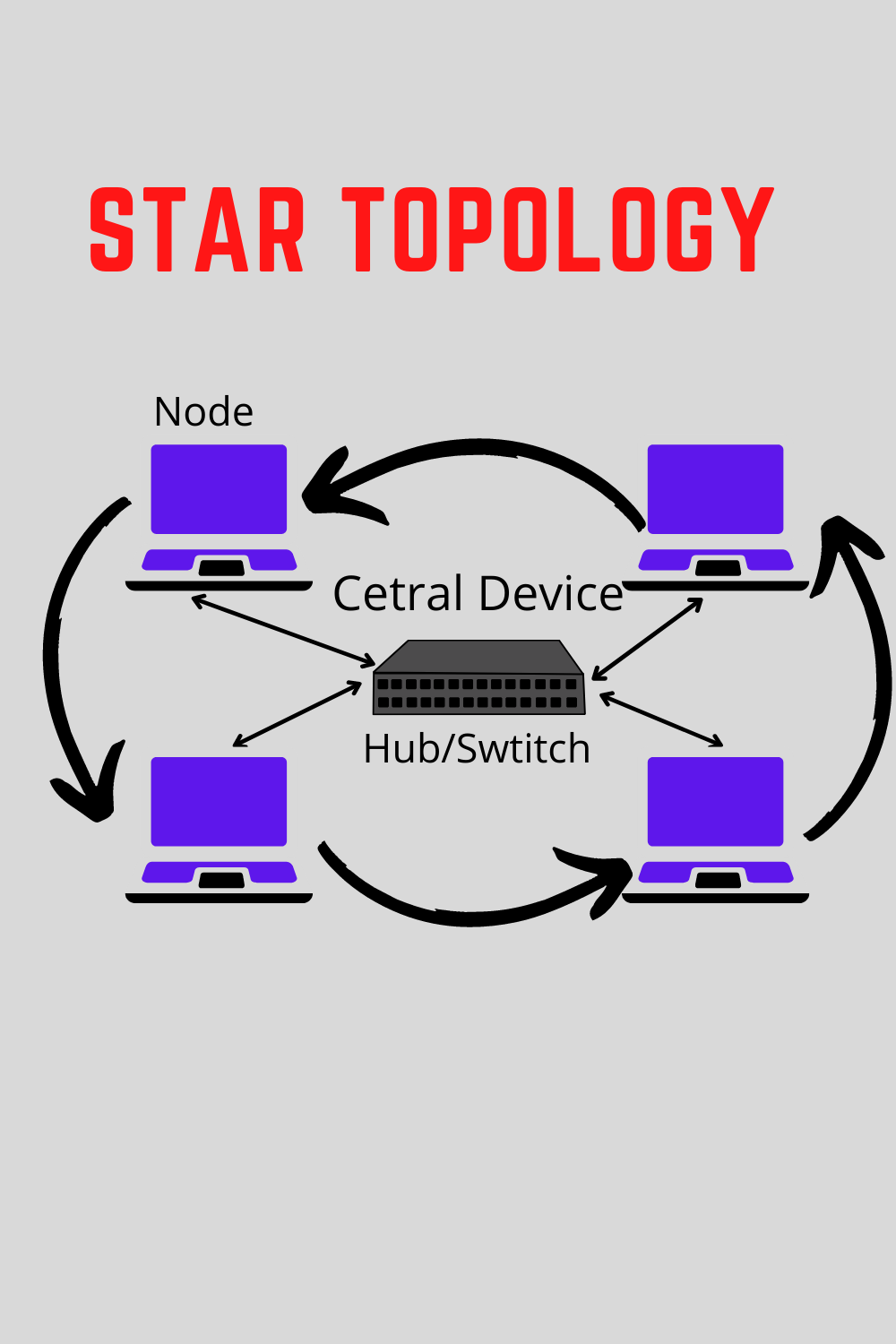
Advantages of star topology
-
Failure of one node will not affect the entire network.
-
Devices can be added, removed, reconfigured, or modified without disturbing the network.
-
Less cabling is needed to configure star topology.
-
Easy to set up and modify.
-
Easy to troubleshoot.
Disadvantages of star topology
-
The entire network is dependent on the central hub: If the hub fails, then the whole network will be down.
-
Expensive to install and use.
-
Performance is solely based on the central hub’s configuration, power, and efficiency
Bus topology
All devices are connected to a central cable called the bus or backbone. A terminator is attached to each to each end of the cable causing signal distortion. As the data passes along the cable each station checks whether the data is addressed to it if the address matches the machine’s address, it receives the data otherwise it rejects it
The network addresses of computers on a network are called the medium access control(MAC) address.
What is network topology
Advantages of bus topology
-
it is easy to install
-
it is less costly
-
Low cost
-
Easy to manage and expand
Disadvantages of bus topology
-
Backbone performance is critical
-
Easily congested on busy periods
-
Efficiency decreases rapidly with each added node
-
Data can only travel in one direction at any point in time
Ring topology
In a ring topology, all devices are connected to one another in the shape of a closed loop. Each station is responsible for regenerating and retransmitting signals around the network to its neighbor.
A token is used to exchange data from one station to another a token can be viewed as an envelope or a bag where data is placed for transmission
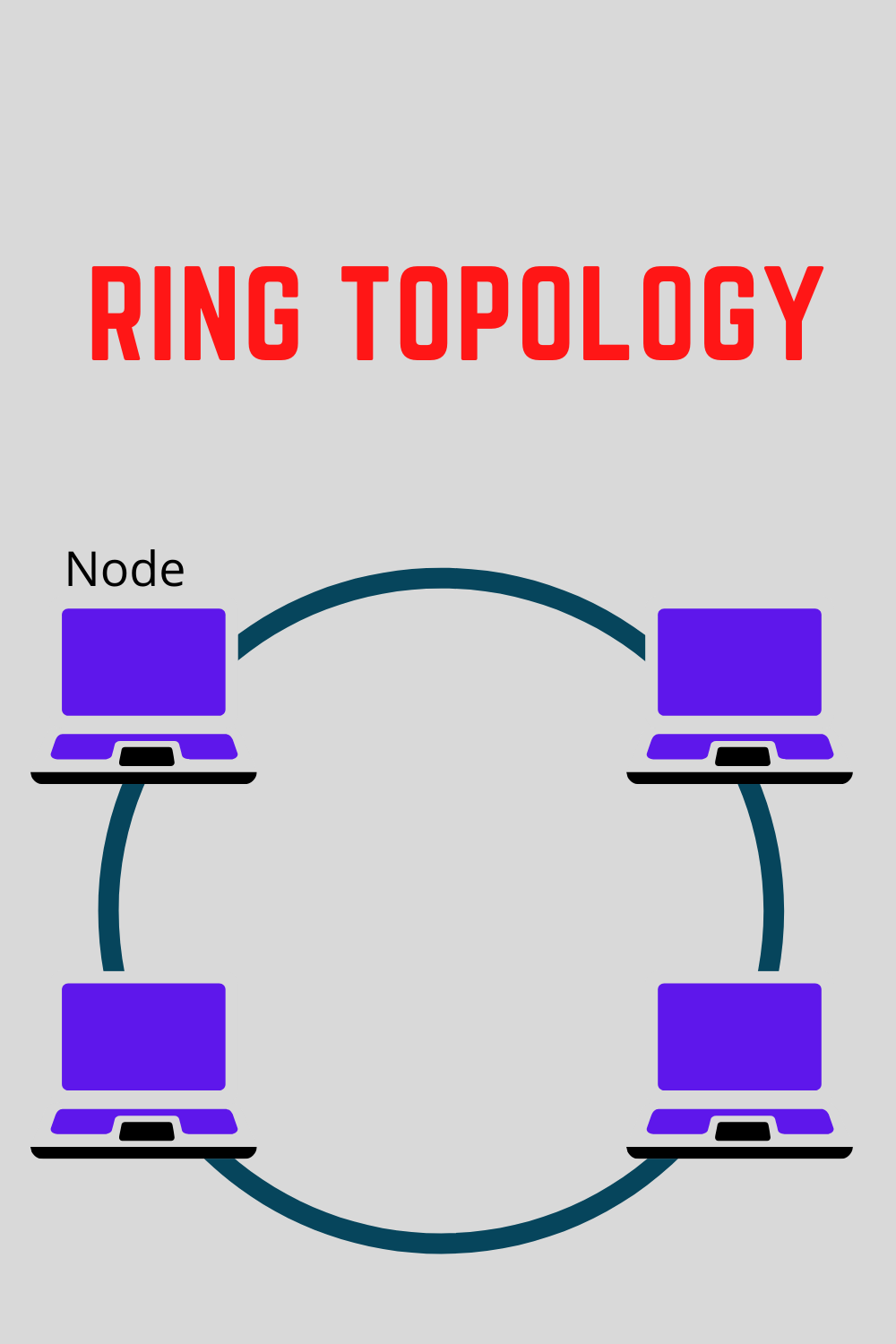
Advantages of ring topology
-
Low incidence of collision
-
Low cost
-
Suitable for small businesses
-
Dual ring option provides continuity through redundancy
Disadvantages of ring topology
-
One faulty node will bring the entire network down
-
Requires extensive preventative maintenance and monitoring
-
Performance declines rapidly with each additional node
Mesh topology
This is the most common type of technology used in a wide-area network where there are many paths between different locations. Devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between the nodes. in a true mesh topology, every node has a connection to every other node in the network.
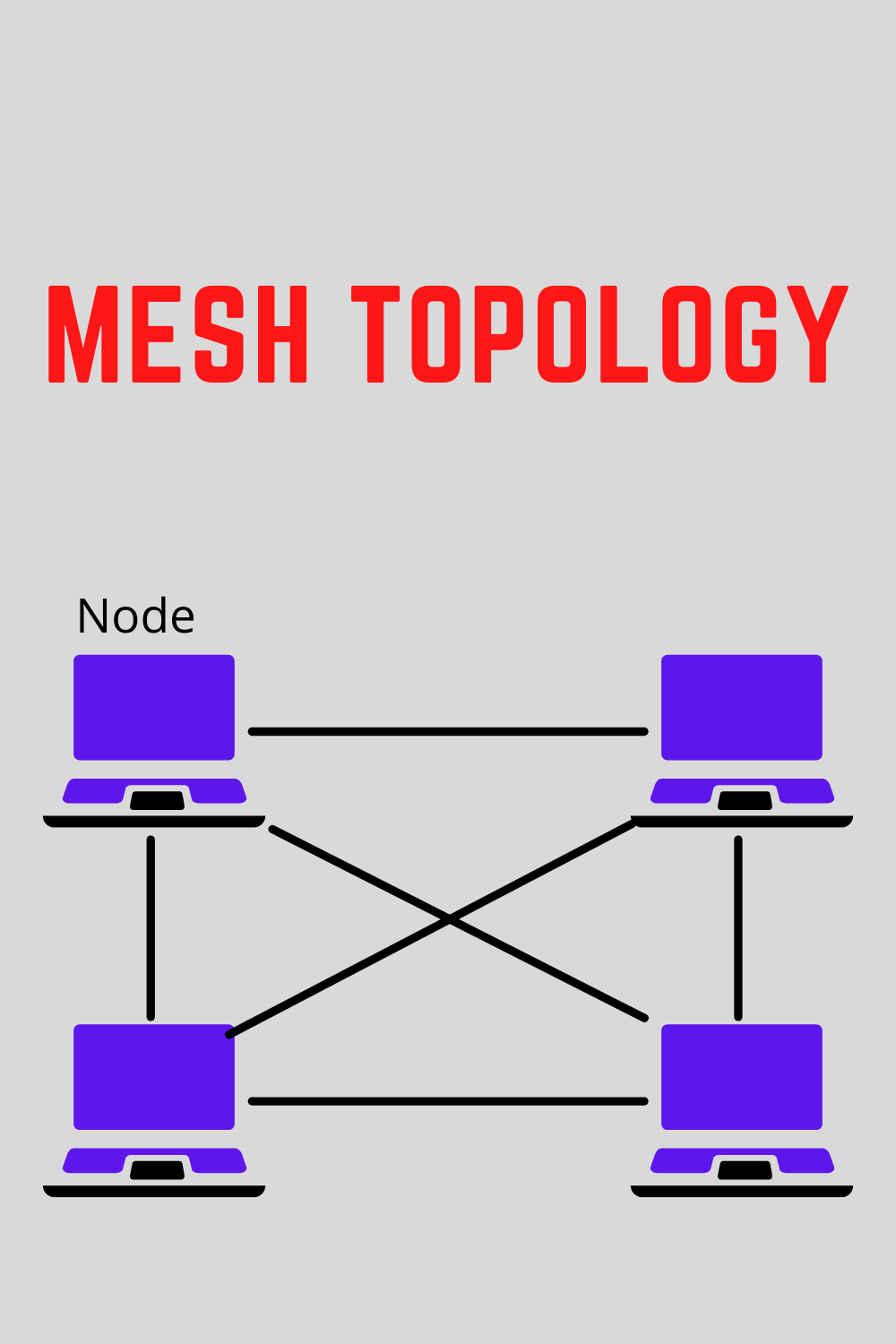
Advantages of mesh topology
-
High speeds data transfers
-
A durable network that isn’t dependent on any one node
-
Very secure
-
Suitable for high-value networks for small to middle-sized networks
-
Easy to identify faulty equipment
Disadvantages of mesh topology
-
Requires a very large amount of cable
-
Can be difficult to secrete all the cable
-
Takes a long time to set up
-
Requires meticulous planning
-
There is a limit to the number of cables each computer can accommodate
Tree/hierarchical topology
As the name suggests, a tree topology network is a structure that is shaped like a tree with many branches. Tree topologies have a root node that is connected to another node hierarchy. The hierarchy is parent-child where there is only one mutual connection between two connected nodes. As a general rule, a tree topology needs to have three levels to the hierarchy to be classified this way. This form of topology is used within Wide Area Networks to sustain lots of spread-out devices
Advantages of tree topology
-
Blends bus and star topologies
-
Easy to manage
-
Easy to expand
-
Suitable for middle-sized businesses
Disadvantages of Tree topology
-
The network is dependent on the health of the root node
-
Requires networking expertise
-
Involves a lot of cables
-
Larger implementations require monitoring software
Hybrid topology
When a topology is composed of two or more different topologies it is referred to as a hybrid topology. Hybrid topologies are most commonly encountered in larger enterprises where individual departments have network topologies that different from another topology in the organization
Advantages of hybrid topology.
-
Offers the easiest method for error detection and troubleshooting
-
Highly effective and flexible networking topology
-
It is scalable so you can increase your network size
Disadvantages of hybrid topology
-
Requires professional management
-
Needs monitoring software
-
Equipment costs are high